Introduction
Navigating tax forms can be overwhelming, but understanding IRS 1040 Schedule 1 is crucial for taxpayers who need to report additional income or claim specific deductions. This supplementary form plays a vital role in ensuring accurate tax filings and maximizing deductions. In this guide, we’ll break down Schedule 1 (Form 1040), its purpose, key components, and how to complete it efficiently.
What Is IRS 1040 Schedule 1?
IRS Schedule 1 is an attachment to the Form 1040, used to report additional income and adjustments to income that are not included on the main tax form. It helps taxpayers disclose earnings beyond wages, such as business income, rental income, and unemployment compensation, while also allowing deductions like student loan interest and self-employment tax.
Why Is Schedule 1 Important?
The IRS introduced Schedule 1 to streamline tax reporting and simplify Form 1040. Instead of cluttering the main tax form with various income sources and deductions, Schedule 1 provides a separate space for these details, ensuring clarity and accuracy in tax filings.
Who Needs to File Schedule 1?
You may need to file Schedule 1 if you:
- Earn self-employment income or freelance earnings.
- Receive rental income or royalties.
- Have unemployment compensation.
- Claim above-the-line deductions, such as educator expenses or health savings account (HSA) contributions.
Breaking Down Schedule 1: Parts & Key Sections
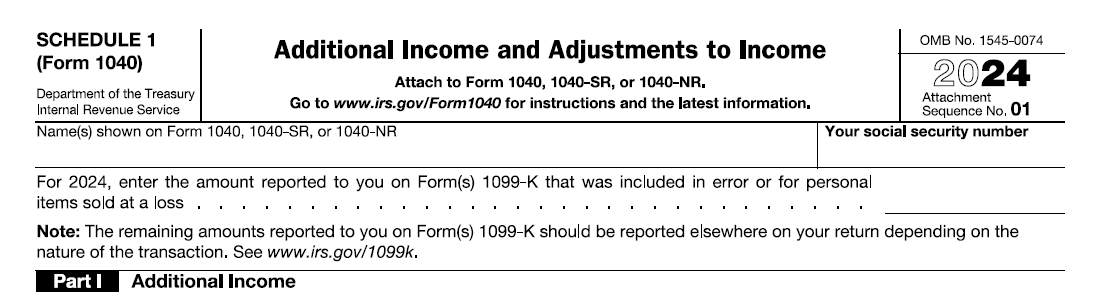
Part I: Additional Income
This section covers various income sources beyond wages and salaries. Some common entries include:
- Taxable refunds, credits, or offsets of state/local income taxes.
- Alimony received (for agreements finalized before 2019).
- Business income or loss (attach Schedule C).
- Rental real estate, royalties, partnerships, S corporations, trusts (attach Schedule E).
- Farm income or loss (attach Schedule F).
- Unemployment compensation.
- Other income, including gambling winnings, jury duty pay, and stock options.
Part II: Adjustments to Income
This section allows taxpayers to claim above-the-line deductions, reducing their adjusted gross income (AGI). Key deductions include:
- Educator expenses (up to $300 for teachers).
- Certain business expenses for reservists, performing artists, and fee-based government officials.
- Health savings account (HSA) contributions.
- Moving expenses (for active-duty military).
- Self-employment tax deductions.
- Student loan interest deduction.
- IRA contributions.
- Tuition and fees deduction (if applicable) .
How to Complete Schedule 1
Step 1: Gather Necessary Documents
Before filling out Schedule 1, ensure you have:
- Form 1099-MISC (for freelance or contract work).
- Form 1099-G (for unemployment benefits).
- Form 1099-K (for third-party payment transactions).
- Receipts for deductible expenses.
Step 2: Fill Out Part I (Additional Income)
Enter any additional income earned throughout the year. If applicable, attach supporting schedules like Schedule C (business income) or Schedule E (rental income).
Step 3: Fill Out Part II (Adjustments to Income)
List deductions that apply to your situation, ensuring you have documentation to support each claim.
Step 4: Transfer Totals to Form 1040
Once completed, transfer the totals from Schedule 1 to the appropriate lines on Form 1040.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Failing to report all income sources (especially freelance earnings).
- Overlooking eligible deductions that could lower taxable income.
- Incorrectly calculating self-employment tax deductions.
- Missing required attachments (e.g., Schedule C for business income).
Optimizing Your Tax Filing Process
To ensure a smooth tax filing experience, consider:
- Using tax software to automate calculations.
- Consulting a tax professional for complex situations.
- Keeping detailed records of income and expenses throughout the year.
Conclusion
IRS 1040 Schedule 1 is an essential form for taxpayers with additional income or adjustments to income. Understanding its components and filing it correctly can help maximize deductions and ensure compliance with IRS regulations. By following this guide, you can confidently complete Schedule 1 and optimize your tax return.